A Guide to Understanding Food Labels
Learn how to decode food labels to make healthier choices and avoid misleading claims with our comprehensive guide.
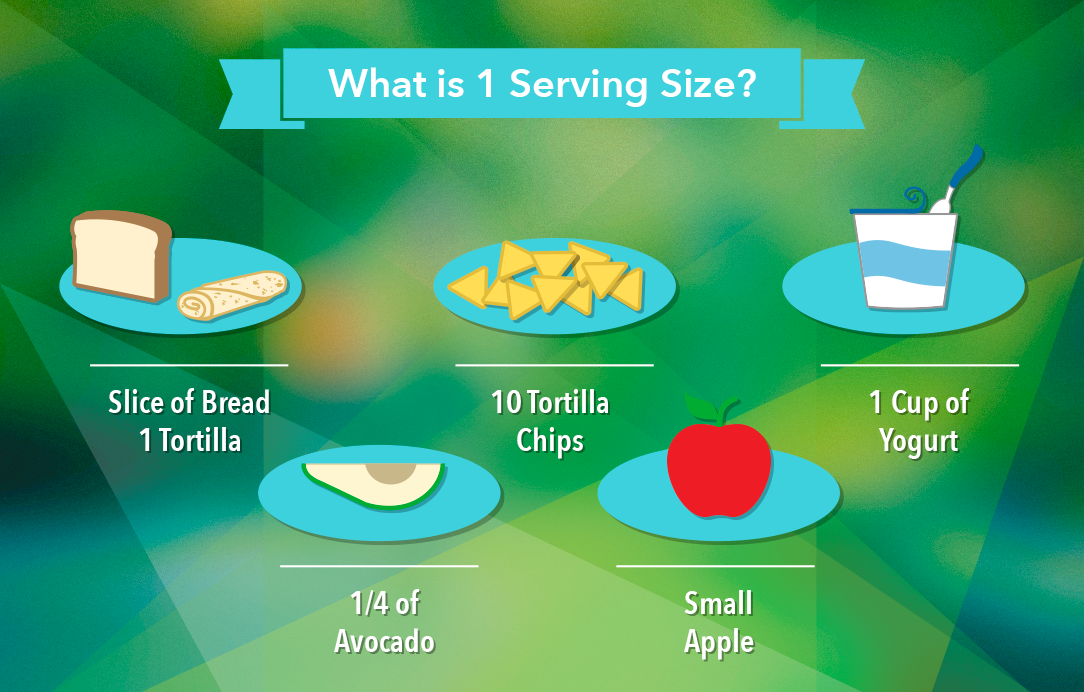
Understanding Serving Sizes
One of the first things to notice on a food label is the serving size. This is crucial because all the nutritional information provided on the label is based on this specific quantity. For example, a serving size might be one cup, but the package could contain multiple servings. This means if you consume the entire package, you need to multiply the nutritional values accordingly. Understanding serving sizes helps in managing portion control and can prevent overeating. It's important to compare the serving size on the label to how much you actually eat to get an accurate picture of your nutritional intake.
Decoding Calories
Calories provide a measure of how much energy you get from a serving of the food. This is often one of the first things people look at when they are trying to manage their weight. The calorie count on a food label can help you determine if a food is high or low in energy. Generally, 40 calories per serving is considered low, 100 calories moderate, and 400 or more high. Keep in mind that if you consume more than one serving, you'll need to multiply the calories accordingly. Monitoring calorie intake is essential for maintaining a balanced diet and a healthy weight.
Nutrients to Limit
Certain nutrients should be limited to maintain a healthy diet. These include saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium. High intake of these can lead to health issues such as heart disease and high blood pressure. Food labels list these nutrients so you can keep track of how much you are consuming. For example, aim to keep your intake of saturated fats and sodium low, as these are often linked to chronic diseases. Understanding these values can help you make healthier choices and avoid foods that may negatively impact your health.
Essential Nutrients to Include
Not all nutrients are bad; some are essential for good health. Nutrients like dietary fiber, vitamins A and C, calcium, and iron are beneficial and should be consumed in adequate amounts. Food labels provide information on these nutrients, helping you to ensure you're getting enough of them in your diet. For instance, dietary fiber is important for digestive health, while calcium is crucial for strong bones. Reading the food label can help you choose foods that are rich in these essential nutrients, contributing to overall well-being.
Understanding Daily Values
The % Daily Value (DV) on a food label shows how much a nutrient in a serving of the food contributes to a daily diet. It is based on a 2,000-calorie diet, which is a general guideline. For example, if the %DV for sodium is 20%, it means that one serving provides 20% of the sodium you should consume in a day. This helps you gauge whether a food is high or low in a particular nutrient. Foods with 5% DV or less are considered low, while those with 20% DV or more are high. Using %DV can guide you in choosing foods that align with your nutritional goals.
Ingredients List
The ingredients list on a food label shows all the ingredients in the product, listed in descending order by weight. This means the first ingredient is the most abundant in the product. Understanding the ingredients list can help you identify what you are consuming and avoid any unwanted additives or allergens. For example, if sugar is listed as the first ingredient, the product is likely high in sugar. Being aware of the ingredients helps you make more informed choices, especially if you are trying to avoid certain ingredients or follow a specific diet.